Medicare Part D consolidation will only get worse with proposed megamergers
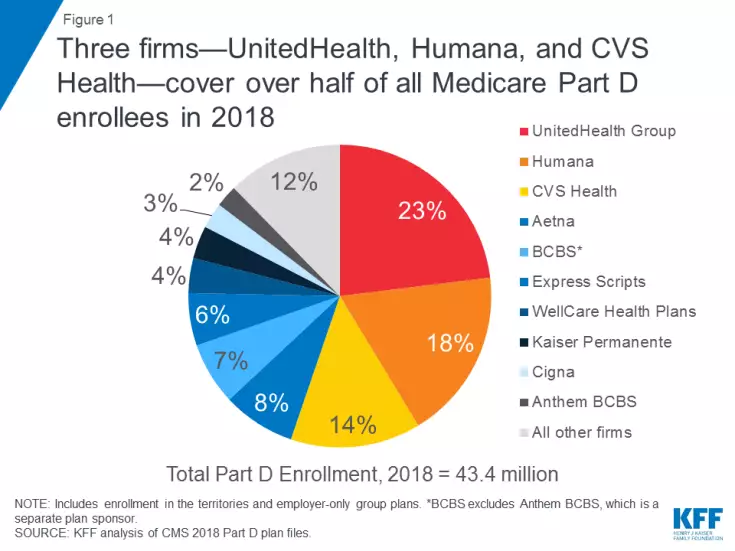
Three sponsors of Medicare Part D plans—UnitedHealth Group, Humana and CVS Health—account for more than half the program’s total enrollment. If proposed mergers involving smaller players like Aetna, Express Scripts and Cigna move ahead, the market would become even more concentrated.
The study, led by Juliette Cubanski, PhD, MPP, MPH, the associate director of the program on Medicare policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation, looked at CMS data on Medicare Part D for 2018—43.4 million of Medicare’s 60 million beneficiaries have prescription drug coverage under the program, with 58 percent covered by a stand-alone prescription drug plan (PDP) and 42 percent in Medicare Advantage drug plans (MA-PDs).
UnitedHealth Group is the market leader, covering 23 percent of all PDP and MA-PD enrollees, followed by Humana (18 percent) and CVS Health (14 percent). The 10 largest Plan D plan sponsors account for nearly 90 percent of enrollment.
Humana and UnitedHealth’s positions could be threatened by pending mergers between some of the biggest Plan D players. CVS would take over the No. 2 spot by combining its market share with Aetna while Cigna and Express Scripts would separate itself from the bottom of the Top 10 with its proposed merger.
“If these mergers go through, four firms—the two merged firms plus UnitedHealth and Humana—would cover 71 percent of all Part D enrollees and 86 percent of stand-alone drug plan enrollees, based on 2018 enrollment,” Cubanski and her coauthors wrote.
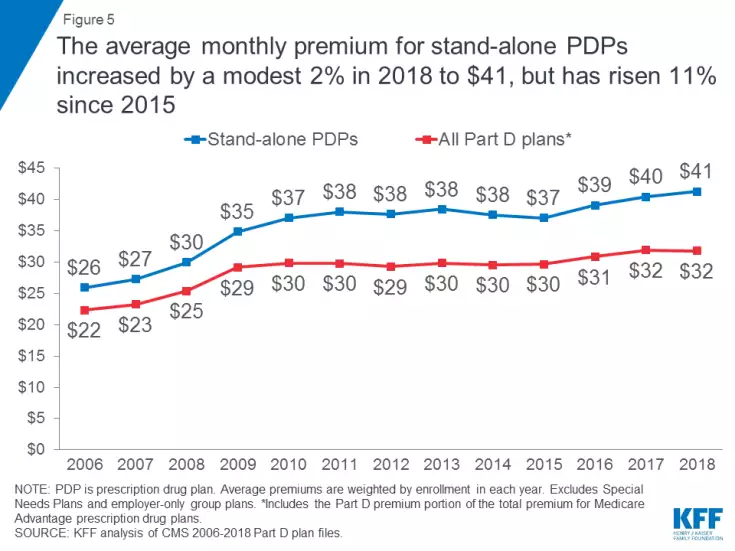
Despite the dominance of a few companies, average monthly premiums for Part D plans haven’t increased at the same rates seen among commercial insurance or on the Affordable Care Act exchanges. PDP enrollees are paying only 2 percent more in 2018, an average of $41 per month, though that represents an 11 percent hike since 2015. The average MA-PD premium is $34 this year.
Among the top five PDPs, the study found an inverse relationship between year-to-year premium hikes and changes in voluntary enrollment among beneficiaries who aren’t receiving low-income subsidies. If premiums go down, enrollment goes up—such as when Aetna’s Medicare Rx Saver plan dropped premiums by $2 and saw enrollment increase by 13 percent.