Hospitals without competition have higher prices
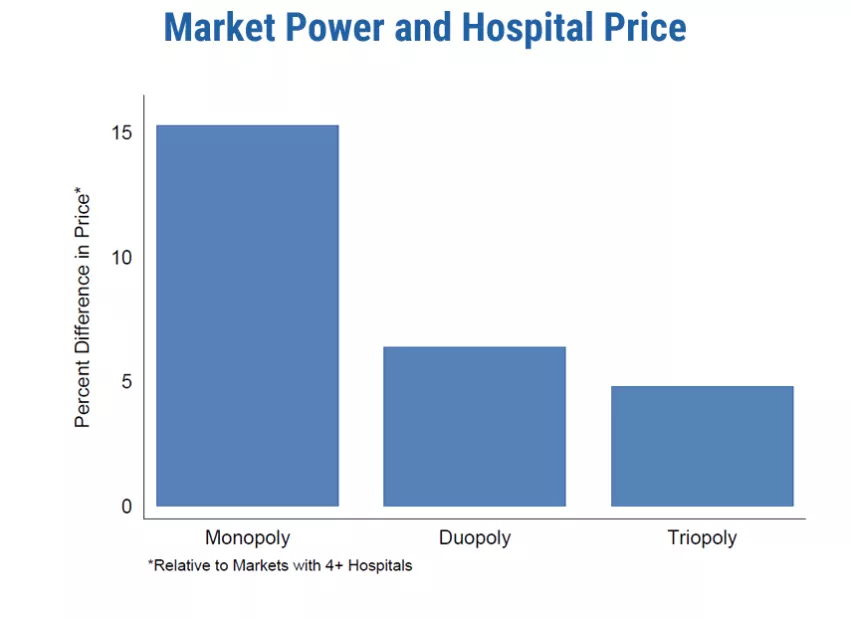
When hospitals enjoy a monopoly in their market, their prices for privately insured patients are 12.5 percent higher on average, according to a study encompassing 88 million people covered by Aetna, Humana and UnitedHealthcare.
The study authors included Yale University health policy and economics professor Zack Cooper, PhD, who said study’s data set, more than two years in the making, allows researchers to better understand what influences health spending by focusing on the privately insured rather than the smaller Medicare population.
For hospitals, the study found the structure of their market strongly influences private insurance spending. In markets with a hospital monopoly, prices are 12 percent higher than those with four or more rivals. The fewer competitors in the market, the higher prices at the remaining hospitals.
Conversely, when the three insurers collectively had a high market share, prices were “significantly lower,” insurers were exposed to less financial risk and more rates were based on Medicare payments.
“A 10 percentage point increase in the insurers’ market share is associated with 7 percent lower prices, 4 percentage points less cases paid as a share of charges, and 6 percentage points more prospectively paid cases that have prices set as a percentage of Medicare payments,” Cooper and his coauthors wrote.
The wave of hospital consolidations allowed the researchers to measure how mergers affect prices. They found location matters—when merging hospitals were less than five miles apart, prices rose by an average of 6 percent. The greater the distance, the lower the post-merger price hikes, with no correlation evident if merging hospitals are more than 25 miles apart.
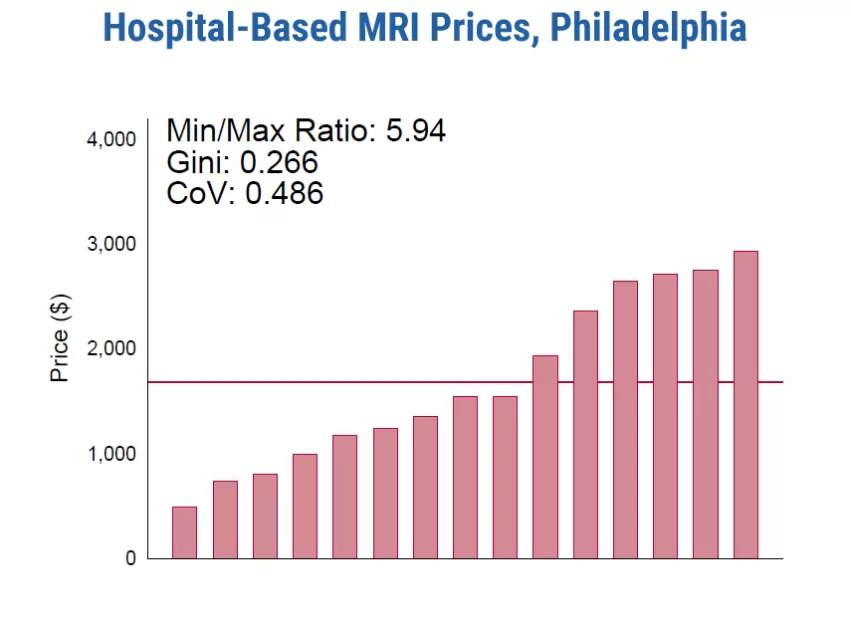
For individual procedures, researchers found substantial variation “even for plausibly undifferentiated services like lower-limb MRIs" within the same hospital market.
Cooper and his coauthors said this would suggest insurers’ bargaining power is a major influence on price negotiations with hospitals.
The results question hospitals’ assertions that mergers and consolidation will end up benefitting patients. Steering patients towards lower-cost care settings could lower spending, but hospitals with few competitors “will able to resist attempts” at payment and delivery reform.
“Our work shows that the consequences of this wave of mergers can be dire for consumer,” said study author Martin Gaynor, a professor at Carnegie Mellon University. “There’s a real need for continued vigorous antitrust enforcement and other policy options to encourage competition and combat market power.”